Drawing Bézier curves
A Bézier curve is a smooth curved line (a spline) that passes through two or more points. A Bézier curves is defined by two anchor points — the curve's end points — and two external control points, called handles. The handles are placed automatically when the control points are drawn. You modify the shape of the curve by moving (dragging) the handles. In Prinect, a handy use of the Bézier curves is for tracing of image contours.
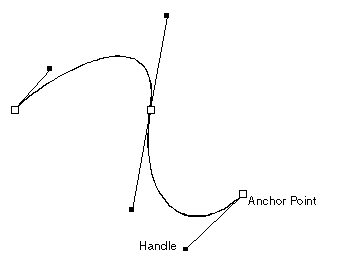
Notes
- When you are drawing a series of connected Bézier curves — for example, to construct a figure rather than a single curve — the second point of a Bézier curve becomes the first point of the next one. When you drag the pointer over the control points of the objects, the control points are highlighted; you can start drawing the next geometric object from such a point.
- An internal anchor point lies on the imaginary line segment that connects its two handles. When you drag any of the handles of an internal anchor point, the anchor point does not change its position; the shapes of the two curves (connected by the anchor point) are modified and the opposite handle moves so that the two handles and the anchor point always lie on one axis.
- During repositioning a Bézier curve, when in the contextual edit bar you enter a value in one of the edit boxes Dx or Dy and then move to the next edit box, Prinect limits the scope of the Bézier curve preview according to the specified value. Consider the following example:
If while repositioning a Bézier curve by dragging, you enter a value of 40 mm for a relative Dx offset distance and then move to Dy, when you point to where you want the Bézier curve to be, Package Designer restricts the movement of the pointer beyond the imaginary vertical borderline that stretches at 40 mm rightward from the original Ox coordinate value of the Bézier curve. To drag the Bézier curve preview freely, in the respective edit box (Dx or Dy) enter 0.00, and then press TAB or ENTER to move to the next edit box.
The zero-value rule is valid only for distance values.